Description of indirect evaporative cooling technology
developed by JSC «GMZ «HIMMASH».
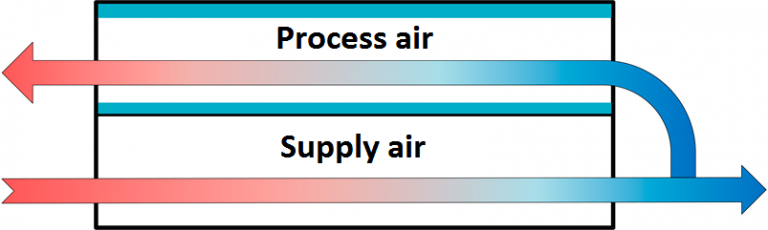
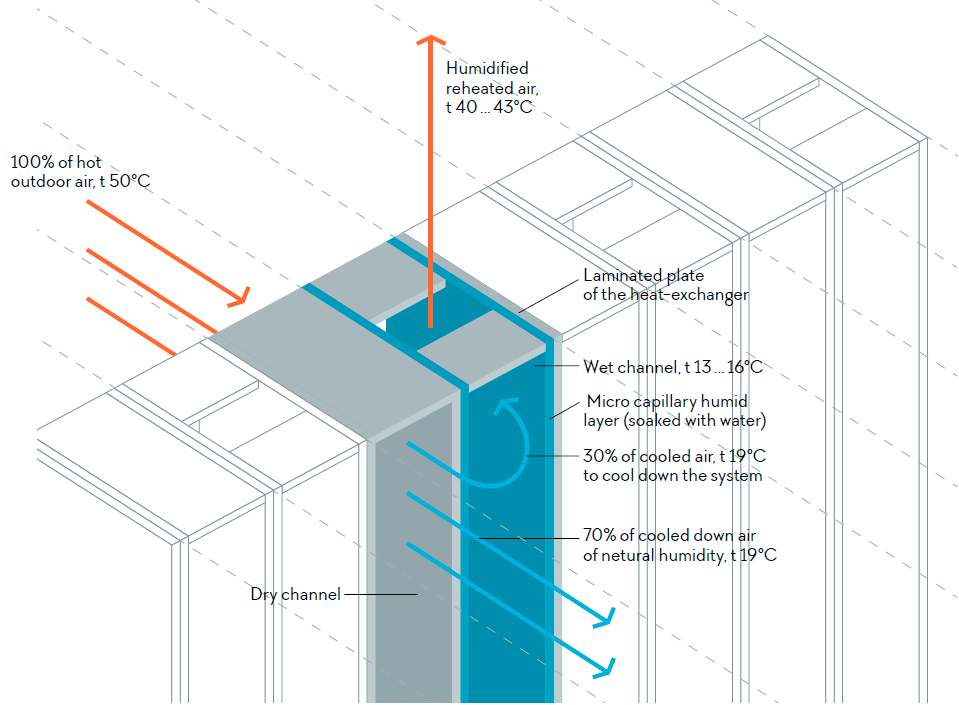
The air enters the air cooling unit, where it passes through the dry channels in full and, ispartially separated into the supply air, which is supplied to the building and process air flow,which is humidified, heated and removed from the heat exchanger.
Plates form two types of channels – the dry channel, in which the cooled air flows, and the wetmicrocapillary channel, in which a part of the cooled air flows countercurrent. The channelsinterchange each other.
The wet channel is constantly saturated with water and transmits a portion ofthe air (30% of the total flow). There is a process of evaporation in it, which is accompanied by a loss of heat. Due to the special scheme of partial air circulation, the surface of the plate cools down through its entire length.
Without direct contact, through the wall, the cold is transferred to theadjacent dry channel, in which hot outer air flows. Thus, at the outlet to the room, there is 70% of the fresh cooled air at a comfortable temperature, without changing the value of natural humidity. The product of the evaporation process, humidified air (30% of the total flow), is released into theatmosphere.
The temperature at the supply channel outlet is conditionally equal to the temperature ofthe wet thermometer for the inlet air estimate indicators. For example, the air at thetemperature of 50°C and humidity of 10% will be cooled in the unit down to 20°C.